Understanding Multichain in Blockchain: A Detailed Insight
- July 20, 2023
- 2034 views
- 12 minutes

Blockchain technology has garnered attention in the technology world for several years. The excitement surrounding blockchain and cryptocurrency shows no signs of slowing down, keeping the buzz alive and thriving.
In earlier days when cryptocurrency had just emerged, blockchain was primarily highlighted for its potential for ensuring decentralized, secure, and anonymous financial transactions. Most importantly, private blockchain development functioned within organizations allowing restricted access to transactions or data on the network.
However, a significant downside of blockchain back then was the isolation of each project because each transaction functioned in a silo, thus separating it from other blockchains.
The advent of multichain technology in the blockchain ecosystem is set to revolutionize this. But how? By connecting independent blockchains together in the same network.
In this article, we are going to walk you through the notion of multichain in a private blockchain, its architecture, setup, creation, mining, and other various aspects.
Table of Contents:
- Defining Multichain in Blockchain
- The Objective of Multichain in Blockchain
- Mechanism of Multichain in Blockchain
- Multichain Blockchain Architecture
- Significant Features of Multichain Blockchain
- Setup of Multichain private blockchain
- Use cases and examples of Multichain in various sectors
- Streaming Concept in Multichain
- Mining in Multichain
- Multichain Rest API
- Future Potential of Multichain
Multichain is an open-source blockchain platform that supports the creation of interconnected yet independent chains within the same network. Each chain operates with its unique rules, permissions, and assets, while seamlessly interacting with other chains. Through peer-to-peer connections facilitated by blockchain nodes, data can be effortlessly transferred between chains, ensuring smooth integration and interoperability.
Multichain emerges as a powerful solution in the blockchain ecosystem with its focus on customizable enterprise blockchains. This cross-chain router protocol (CRP) allows users to bridge tokens across multiple blockchains.
It is interesting to note that this project, founded in July 2020, can support more than 74 independent chains which include BNB smart chain, Harmony, and Fantom.
With the support of cross-chain bridges and cross-chain routers, users can effortlessly transfer their assets between blockchains in a seamless manner. Further, Multichain introduced its governance token, MULTI, allowing token holders to actively engage in the project’s future governance initiatives.
The primary goal behind the creation of Multichain is to ensure transaction visibility among the network participants while still maintaining user privacy. Transparency in transactions while maintaining control and stability makes the implementation of multichain a must in businesses or organizations.
Multichain boasts a lightweight private network with user-friendly tools, making it effortless to create and manage. With support for multiple programming languages, blockchain developers have the flexibility they need. The platform also facilitates the seamless creation and transfer of native tokens, enabling users to exchange assets within the network.
Simply put, Multichain aims to provide a readily accessible blockchain network that incorporates key features of Bitcoin for the development of wallet applications. Multichain ensures compatibility with diverse Bitcoin-related applications and open-source platforms through an extended Bitcoin API and platform. Rather than enforcing uniformity, the network nodes simply require linkage and offer flexibility in their configuration.
Therefore, by embracing multichain blockchain technology, all participating systems within an organization or across multiple organizations converge into a unified network. This integration ensures efficient collaboration and enables sharing of a common transaction database, which fosters connectivity and enhances efficacy.
At the basic level, the linking of two blockchain nodes on a decentralized peer-to-peer network is known as multichain. The two individual chains have their set of rights, rules, and permissions which are represented by an address.
Each node in the network allows seamless transfer of data with flawless interoperability and integration. The multichain platform is more inclined toward the creation of customized enterprise blockchains.
Another advantage of a multichain system is that if one node gets unsatisfactory responses from other users, the P2P connection gets terminated. For multichain development in blockchain, the process of connecting two blockchain nodes is termed as handshaking.
Bridging of tokens with smart contracts
Multichain renders two methodologies to bridge tokens, one of them is leveraging smart contracts to lock tokens on a blockchain and minting wrapped or pegged coins on another blockchain. It uses a standardized crypto-pegging mechanism for bridging tokens and coins.
For instance, for bridging BNB from the BNB Smart chain to another chain, say Ethereum, Multichain will lock the BNB coin in a smart contract and mint a wrapped BNB token on the Ethereum blockchain in a 1:1 ratio.
Bridging of tokens is possible in Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and other selected blockchain networks like Terra and Cosmos. The same process is adopted for NFTs as well tokens are issued on the new blockchains.
Bridging of tokens using liquidity pools
Another method used to bridge tokens in a multichain is coin swapping. Some popular tokens like USDC exist in multiple blockchains in their native forms. So, to bridge these tokens, you need to know someone to know who is ready to trade your coin with the coin you want. This process of using liquidity pools also allows other users to provide their tokens for exchange.
Read More : A Complete In-Depth Guide To Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
The fundamental design of multichain architecture is similar to that of Bitcoin Core, and so, if you understand Bitcoin Core, you can get the idea of multichain better.
Multichain has two primary subsystems – node and wallet. The node is to track the global state of the chain and wallet to hold private keys securely and track transactions to the node. Both the node and wallet work on independent mechanisms to store and retrieve information.
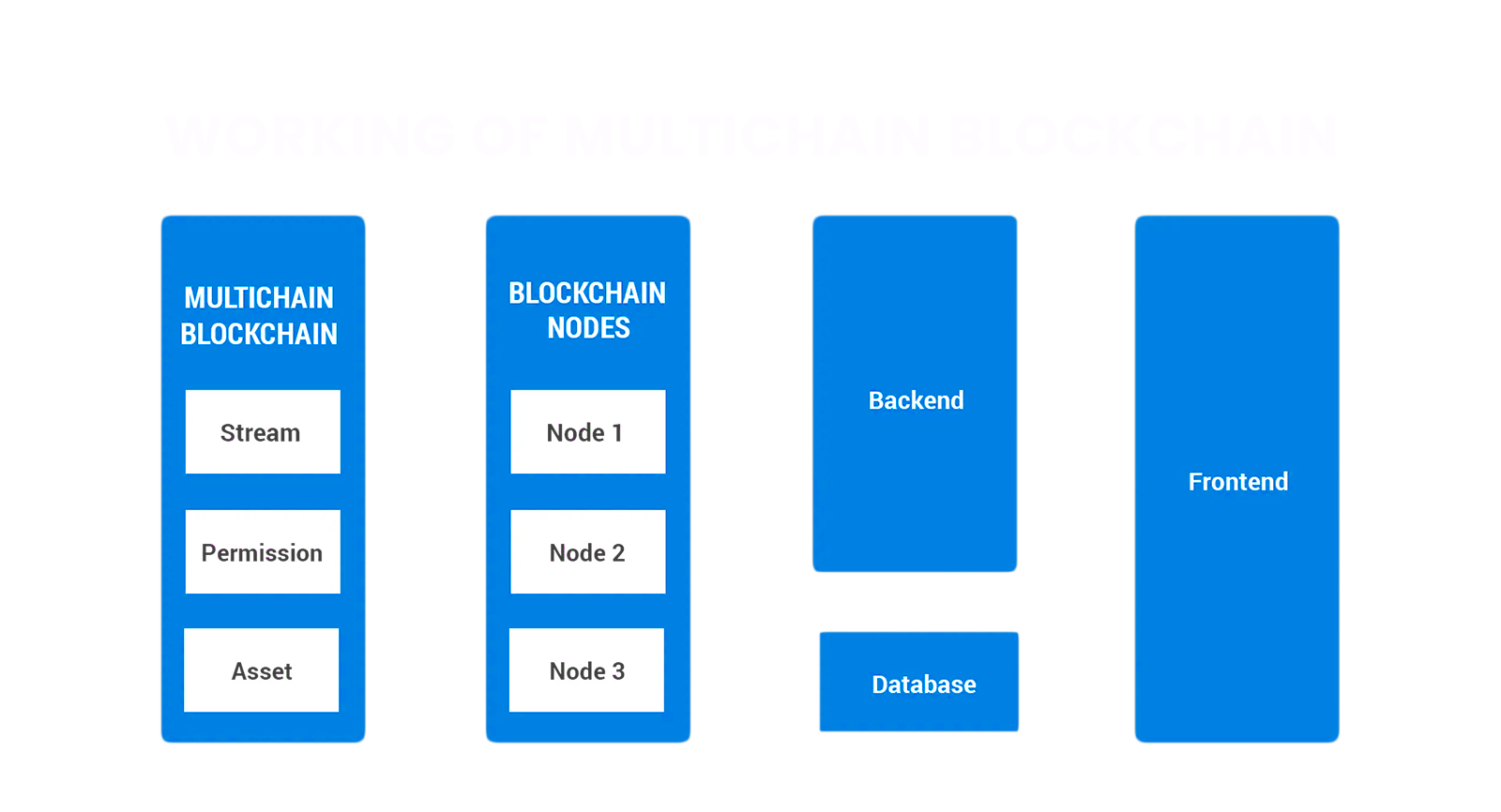
The nodes in the multichain network have their own APIs with which they are connected to applications. The chain comprises permissions for information, streams, and assets. The “setup phase” in a multichain includes only the first few blocks.
Multichain and Traditional Blockchain: Architecture Compared
Let’s take a look at the aspects where multichain architecture differs from traditional blockchain.
- Scalability – Traditional blockchain architecture is based on a single blockchain where transactions are recorded. On the contrary, multichain relies on more than one blockchain for transaction records and these can be customized as per specific applications or use cases.
- Customization – Multichain allows for customization where each blockchain can be configured by the developers to meet the business requirements. Meanwhile, standard blockchain requires developers to meet the platform specifications and cannot be customized.
- Interoperability – In a multichain technology, different blockchains can connect with each other to facilitate data exchange. Traditional blockchain doesn’t communicate with other blockchains as it operates in isolation from other chains.
- Privacy – Multichain technology offers greater privacy compared to traditional blockchain architectures. Private blockchains created using multichain technology restrict access to sensitive data and make the system more secure for permissioned users.
Components of Multichain Architecture
The multichain platform provides a user-friendly API with a command-line interface to facilitate seamless transactions. It comprises a suite of comprehensive business solutions like permissions management, native assets, and per-chain customization.
Layers of Multichain Architecture
Multichain architecture has a base layer that has two segments – the backend and the database layer. While the backend mainly handles network security and the foundations, the database is responsible for maintaining a record of the transactions done and permissions.
The next layer is the blockchain nodes that support peer-to-peer connectivity between multiple blockchains and enable effortless transfer of data or information between nodes in the chain. This layer is also called the front end whose simple and easy-to-use interface is mostly useful for developing decentralized finance (Defi) applications.
Multichain technology allows businesses to build a blockchain as per their business needs. This versatile platform goes beyond the basics of blockchain and offers standout features that are designed to streamline transactions and operations in businesses. The key features of Multichain in Blockchain are as follows.
- Unconstrained Assets – Multichain allows the creation of native tokens or assets that are trackable at the blockchain level. In multichain, users have the ability to authorize and verify a large number of unconstrained assets on the ledger. Moreover, multichain supports transactions of multiple assets between multiple parties.
- Permissions Management – If your business demands a permissioned environment for your users to connect and make transactions, multichain blockchain is the answer. Also, users can create assets and new data streams on the chain. This finely-tuned permission management permits business entities to operate in either a public or private network.
- Data Streams – Multichain provides extensive support for data sharing, data encryption, timestamping, digital signatures, and archiving. This feature allows you to generate limitless data streams with multiple key values in various time series. Streams can be public or private or made accessible to a specific group of users.
- Speed & efficiency – Another advantage of multichain is that it allows an easy and rapid fast development process where users can quickly connect to new blockchain with a permissioned network and operate efficiently.
- Scalability – The mechanism for storing data in a multichain is dual chain which implies that publicly available data can be stored either on the chain or off the chain as demanded by the enterprise. Unlike traditional blockchain, information is not stored and copied on all the nodes of the chain. Only those with permission to view the dataset can be given access to the private decryption key.
- Peer-to-peer connectivity – The communication between nodes on the multichain is called handshaking where each node has a unique address with permission. As a consequence, nodes exchange messages with each other, and on receiving unsatisfactory messages, the P2P connection gets discontinued.
This segment of this article focuses on the creation of a private blockchain using multichain. Multichain is useful for creating and managing private and permissioned blockchains. Here is an overview of the process of Multichain private blockchain setup.
Step 1 – Multichain installation
After downloading the appropriate multichain binaries from the official website, you need to install the multichain on the server where you plan to run and operate the private blockchain.
Step 2 – Creating a New Blockchain
The next thing you need to do is create a new directory for your blockchain configuration and data. Here you can use a multichain-util command-line tool for building the chain, specifying its name, data directory path, and other parameters associated with it.
Step 3 – Blockchain configuration
Configure your blockchain parameter tailored to your specific requirements which include setting mining parameters, consensus rules, and other blockchain-specific options. After setting up the configuration, you can create or import all the permissioned addresses that can participate in the private blockchain.
Step 4 – Start the blockchain
Multichain blockchain is deployed using multichaind command by entering the name of the blockchain created in the third step. The blockchain will start and you will be able to see the process of blockchain creation, its logs, and information.
Step 5 – Interact with blockchain
To interact with the blockchain for various purposes like sending transactions, managing permissions, and querying the blockchain, you can use the Multichain command-line interface (CLI) or API.
Step 6 – Configure Mining and Consensus (Optional)
If you want to mine (proof-of-work) or customize the consensus mechanism, it can be done by modifying the configuration set up for the blockchain.
Step 7 – Configure Access Control (Optional)
You can allow different permissions for reading, writing, and mining on the blockchain by configuring custom access controls for different addresses.
Step 8 – Security and Encryption (Optional)
Encryption of data stored on the blockchain to enhance security is possible depending on your specific requirements.
Step 9 – Backup and maintain
After creating your private blockchain in Multichain, it is important to regularly back up your data on the private blockchain to prevent any kind of data loss.
Since Multichain offers room for customization of blockchain networks, it has become an integral technology to adopt for specific use cases in diverse industries. With the support of multichain, developers can create tailor-fit blockchains with certain and unique rules, assets, and permissions.
Multichain has been implemented by multiple organizations like Chainstack, Wolfram, and SAO. SAO creates new private networks and provides restricted access to the blockchain to its clients. Wolfram’s language model now incorporates Multichain which allows users to build block-chain-based applications effortlessly.
The stream concept of multichain focuses on data retrieval, archiving, and timestamping. It can be used to implement 3 types of databases on a chain.
- Document store or key-value database – Following the style of NoSQL.
- A time series database – The order of the entries is highlighted
- An identity-driven database – Entries are categorized according to their authors.
Multichain blockchain is useful for creating any number of streams comprising items with the basic attributes which are mentioned below.
- Publishers (one or more) who have put their digital signatures.
- Optional key for data retrieval in the future as per convenience.
- Data – which can be anything from a small text to a large file with megabytes.
- The timestamp that is recorded from the block header where an item is confirmed.
Streams can be integrated into Multichain’s permission system in a variety of ways. This also implies one can create streams only if permission is provided to do so just like assets are issued by certain addresses. Streams can be open or closed. Anyone having permission to carry out transactions on the blockchain can create open streams. However, closed streams are restricted to only the list of permissioned addresses which is modifiable.
Mining in Multichain is carried out through distributed consensus algorithms where miners are identified according to their predetermined set of entities with a mining diversity measure implemented having a value between 0 and 1. This distributed consensus approach is used for mining by a group of network administrators.
The following procedures are incorporated to ensure the efficacy of a block.
- Applying permissions modifications through transactions and blocks.
- Determining the total number of approved miners after revisions
- Rounding up the number of miners and multiplying it by the variety of mining.
The Multichain Rest API is a powerful gateway to facilitate interaction with Multichain. With this API, developers can seamlessly communicate with other blockchains on the multichain and execute transactions. It allows access to critical and sensitive data on the blockchain networks in a secure and streamlined manner.
The user-friendly interface of the Multichain Rest API helps in the process of integration of blockchain functionalities into various other applications. Whether you need to build a financial solution, develop dApps, or supply management tools, the multichain API provides access to all the necessary tools required to harness the full potential of multichain technology.
With the help of this Rest API, users can manage their permissions securely, customize the parameters on the blockchain, and handle native assets, to tailor the blockchain network according to your business-specific requirements.
In addition to this, this API allows smooth and easy integration with the existing blockchain system which in turn promotes scalability and efficiency.
To conclude, the Multichain Rest API is immensely beneficial for blockchain developers because it offers a simplified and secure way to connect and communicate with other blockchain networks in the multichain.
Read More: Introduction to Private Blockchain: A Beginner’s Guide
Multichain, being a highly adaptable and scalable technology, is more and more adopted by businesses of various industries. In fact, it is helping them transform into high-growth sectors by mastering the technology and ways to eliminate complications.
Multichain is the future of blockchain where we can expect finance, banking, insurance, and other sectors to make the most of this high-end technology. With this multichain strategy, executing complicated transactions and data transmission will become not only very easy but also fast and secure.
The Web3 evolution will soon see an inrush of billions of users and in such a scenario, it becomes crucial that you prepare your business for this multichain strategy to speed up transaction processes and deliver a frictionless experience to your end users.
Closing Thoughts
The key takeaway is that Multichain technology is useful for businesses because this platform offers several standout features and exceptional benefits. They can launch private and interoperable customized blockchains where every chain can interact with others, execute transactions and transmit data seamlessly. Besides easy data sharing and faster transactions, the multichain platform also offers high-grade security to the users.
It boasts an extensive array of bridgeable tokens, aiming to become the prime Web3 router. For DeFi enthusiasts seeking seamless transitions between networks like Solana (SOL), Avalanche (AVAX), and Ethereum (ETH), Multichain offers a simple solution.
You can also learn more about private blockchain, cryptocurrency, crypto trading, etc. from qualified professionals of Webgen Technologies, a reputed blockchain development company in the USA. We can assist you in your decentralized adventure with cutting-edge solutions.